Merkle Tree API Documentation (Golang)
This is the Golang version of the Merkle Tree API Documentation (C++ documentation). It mirrors the structure and functionality of the C++ version, providing equivalent APIs in Golang. For more detailed explanations, refer to the C++ documentation.
To see a complete implementation, visit the Hash and Merkle example for a full example.
Using the Hash package requires go version 1.22
Tree Structure and Configuration in Golang
Defining a Merkle Tree
/// * `layerHashers` - A vector of hash objects representing the hashers of each layer.
/// * `leafElementSize` - Size of each leaf element.
/// * `outputStoreMinLayer` - Minimum layer at which the output is stored.
///
/// # Returns a new `MerkleTree` instance or EIcicleError.
func CreateMerkleTree(
layerHashers []hash.Hasher,
leafElementSize,
outputStoreMinLayer uint64,
) (MerkleTree, runtime.EIcicleError)
The outputStoreMinLayer parameter defines the lowest layer that will be stored in memory. Layers below this value will not be stored, saving memory at the cost of additional computation when proofs are generated.
Building the Tree
The Merkle tree can be constructed from input data of any type, allowing flexibility in its usage. The size of the input must align with the tree structure defined by the hash layers and leaf size. If the input size does not match the expected size, padding may be applied.
Refer to the Padding Section for more details on how mismatched input sizes are handled.
/// * `mt` - The merkle tree object to build
/// * `leaves` - A slice of leaves (input data).
/// * `config` - Configuration for the Merkle tree.
///
/// # Returns a result indicating success or failure.
func BuildMerkleTree[T any](
mt *MerkleTree,
leaves core.HostOrDeviceSlice,
cfg core.MerkleTreeConfig,
) runtime.EIcicleError
Tree Examples in Golang
Example A: Binary Tree
A binary tree with 5 layers, using Keccak-256:
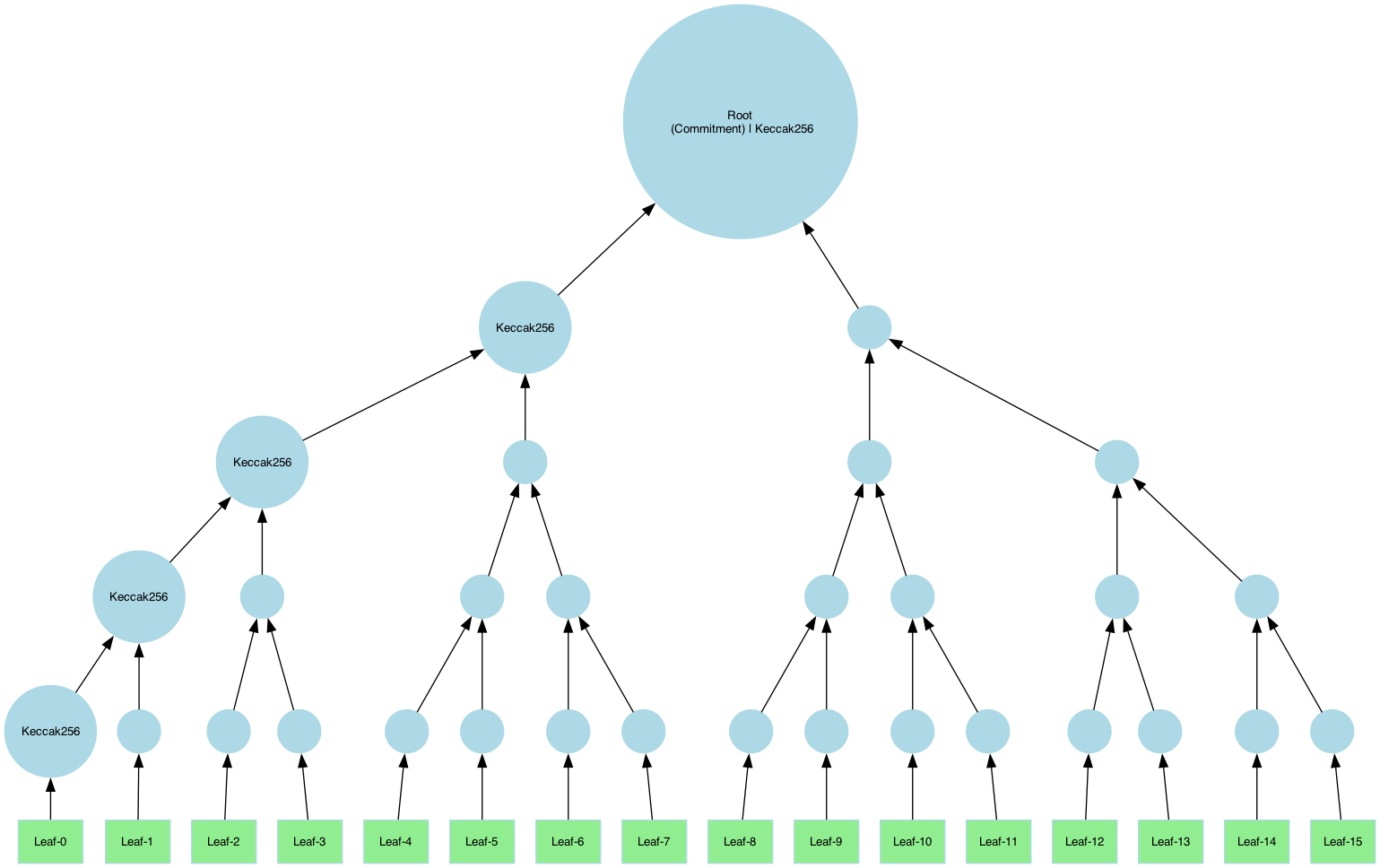
import (
"github.com/ingonyama-zk/icicle/v3/wrappers/golang/core"
"github.com/ingonyama-zk/icicle/v3/wrappers/golang/hash"
merkletree "github.com/ingonyama-zk/icicle/v3/wrappers/golang/merkle-tree"
)
leafSize := 1024
maxInputSize := leafSize * 16
input := make([]byte, maxInputSize)
hasher, _ := hash.NewKeccak256Hasher(uint64(leafSize))
compress, _ := hash.NewKeccak256Hasher(2 * hasher.OutputSize())
layerHashers := []hash.Hasher{hasher, compress, compress, compress, compress}
mt, _ := merkletree.CreateMerkleTree(layerHashers, uint64(leafSize), 0 /* min layer to store */)
merkletree.BuildMerkleTree[byte](&mt, core.HostSliceFromElements(input), core.GetDefaultMerkleTreeConfig())
Example B: Tree with Arity 4
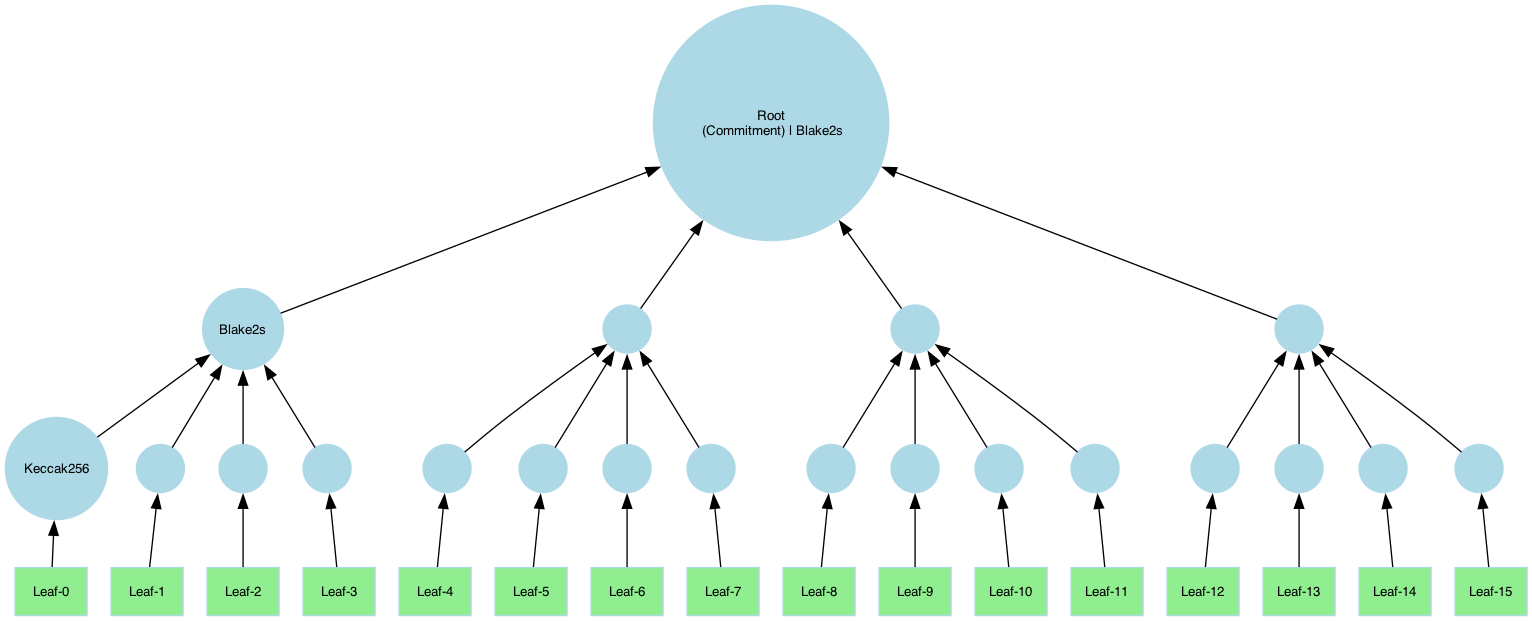
This example uses Blake2s in upper layers:
// define layer hashers
// we want one hash layer to hash every 1KB to 32B then compress every 128B so only 2 more layers
hasher, _ := hash.NewKeccak256Hasher(uint64(leafSize))
compress, _ := hash.NewBlake2sHasher(2 * hasher.OutputSize())
layerHashers := []hash.Hasher{hasher, compress, compress,}
mt, _ := merkletree.CreateMerkleTree(layerHashers, uint64(leafSize), 0 /* min layer to store */)
merkletree.BuildMerkleTree[byte](&mt, core.HostSliceFromElements(input), core.GetDefaultMerkleTreeConfig())
Padding
When the input for layer 0 is smaller than expected, ICICLE can apply padding to align the data.
Padding Schemes:
- Zero padding: Adds zeroes to the remaining space.
- Repeat last leaf: The final leaf element is repeated to fill the remaining space.
// type PaddingPolicy = int
// const (
// NoPadding PaddingPolicy = iota // No padding, assume input is correctly sized.
// ZeroPadding // Pad the input with zeroes to fit the expected input size.
// LastValuePadding // Pad the input by repeating the last value.
// )
import (
"github.com/ingonyama-zk/icicle/v3/wrappers/golang/core"
)
config := core.GetDefaultMerkleTreeConfig();
config.PaddingPolicy = core.ZeroPadding;
merkletree.BuildMerkleTree[byte](&mt, core.HostSliceFromElements(input), core.GetDefaultMerkleTreeConfig())
Root as Commitment
Retrieve the Merkle-root and serialize.
/// Retrieve the root of the Merkle tree.
///
/// # Returns
/// A reference to the root hash.
func GetMerkleTreeRoot[T any](mt *MerkleTree) ([]T, runtime.EIcicleError)
commitment := merkletree.GetMerkleTreeRoot[byte](&mt)
fmt.Println!("Commitment:", commitment)
The commitment can be serialized to the proof. This is not handled by ICICLE.
Generating Merkle Proofs
Merkle proofs are used to prove the integrity of opened leaves in a Merkle tree. A proof ensures that a specific leaf belongs to the committed data by enabling the verifier to reconstruct the root hash (commitment).
A Merkle proof contains:
- Leaf: The data being verified.
- Index (leaf_idx): The position of the leaf in the original dataset.
- Path: A sequence of sibling hashes (tree nodes) needed to recompute the path from the leaf to the root.
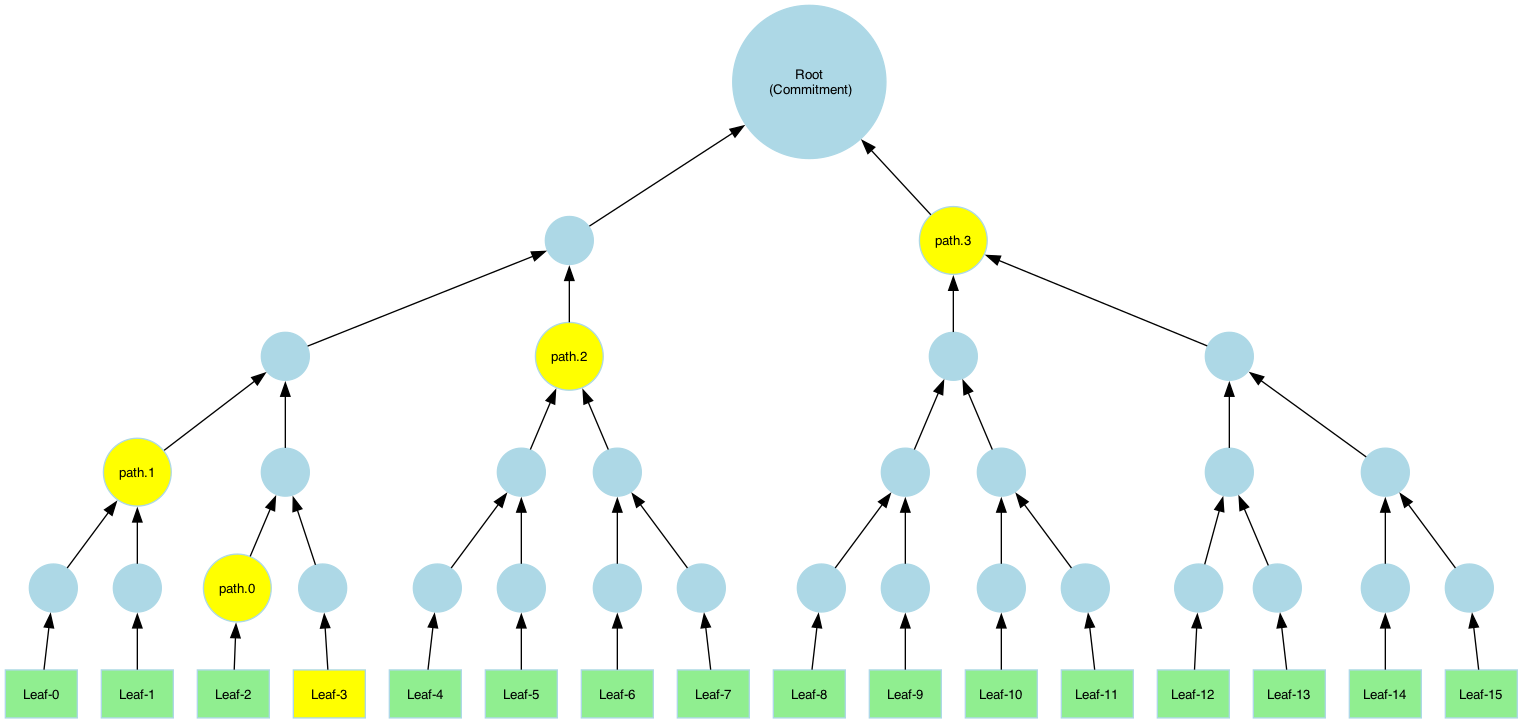
/// * `leaves` - A slice of leaves (input data).
/// * `leaf_idx` - Index of the leaf to generate a proof for.
/// * `pruned_path` - Whether the proof should be pruned.
/// * `config` - Configuration for the Merkle tree.
///
/// # Returns a `MerkleProof` object or eIcicleError
func GetMerkleTreeProof[T any](
mt *MerkleTree,
leaves core.HostOrDeviceSlice,
leafIndex uint64,
prunedPath bool,
cfg core.MerkleTreeConfig,
) (MerkleProof, runtime.EIcicleError)
Example: Generating a Proof
Generating a proof for leaf idx 5:
mp, _ := merkletree.GetMerkleTreeProof[byte](
&mt,
core.HostSliceFromElements(input),
5, /* leafIndex */
true, /* prunedPath */
core.GetDefaultMerkleTreeConfig(),
)
The Merkle-path can be serialized to the proof along with the leaf. This is not handled by ICICLE.
Verifying Merkle Proofs
/// * `proof` - The Merkle proof to verify.
///
/// # Returns a result indicating whether the proof is valid.
func (mt *MerkleTree) Verify(mp *MerkleProof) (bool, runtime.EIcicleError)
Example: Verifying a Proof
isVerified, err := mt.Verify(&mp)
assert.True(isVerified)
Pruned vs. Full Merkle-paths
A Merkle path is a collection of sibling hashes that allows the verifier to reconstruct the root hash from a specific leaf. This enables anyone with the path and root to verify that the leaf belongs to the committed dataset. There are two types of paths that can be computed:
- Pruned Path: Contains only necessary sibling hashes.
- Full Path: Contains all sibling nodes and intermediate hashes.
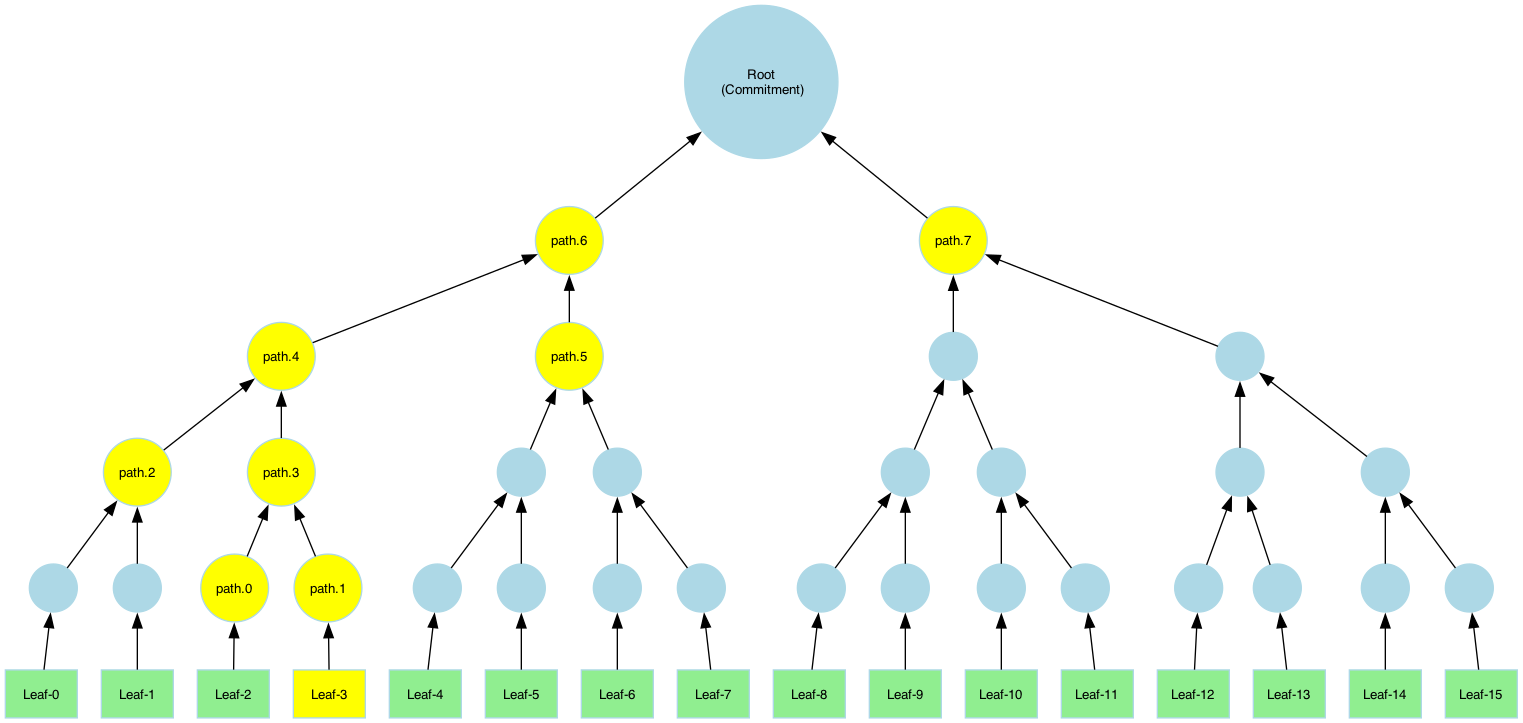
To compute a full path, specify pruned=false:
mp, _ := merkletree.GetMerkleTreeProof[byte](
&mt,
core.HostSliceFromElements(input),
5, /* leafIndex */
false, /*non-pruned is a full path --> note the pruned flag here*/
core.GetDefaultMerkleTreeConfig(),
)
Handling Partial Tree Storage
In cases where the Merkle tree is large, only the top layers may be stored to conserve memory. When opening leaves, the first layers (closest to the leaves) are recomputed dynamically.
For example to avoid storing first layer we can define a tree as follows:
mt, err := merkletree.CreateMerkleTree(layerHashers, leafSize, 1 /*min layer to store*/);